|
|
|
Main menu
HELP
|
Abstracts of presentations
M17 supports both voice and data streams. A reference C implementation is available at GitHub, licensed under GNU GPL-2.0. The presentation will cover technical details of the protocol's RF stack. M17 demo transceivers built with GNU Radio, USRP B210, and other hardware will then be presented to the audience. Main website: https://m17project.org Twitter feed: https://twitter.com/m17_project GitHub: https://github.com/M17-Project/M17_Implementations/tree/main/SP5WWP and the GNU Radio compatible block https://github.com/M17-Project/gr-m17
We report the use of GNU Radio to realize multiheterodyne spectroscopy of Eu3+:Y2SiO5crystal at cryogenic temperature. The flexible multiheterodyne scheme developed by GNU Radio also has the potential to be applied in other applications for precise physical state probing. Proceeding of the presentation (PDF format)
In this presentation you will see how to synchronize a Vertical Incidence Pulsed Ionospheric Radar (VIPIR) and an Ionospheric Echoes Receiver (IER), made of an USRP N200, using GNU Radio Companion 3.8 and a generator pulse circuit, which will send one pulsed signal (trigger) in a specific time to beginning the transmission. It is used a GPSDO by the Ionospheric Echoes Receiver to set its time by NMEA's in the reception. Furthemore, you will see how the use of message passing and tags programmed in out of tree blocks affect the synchronization in the acquisition of ionospheric echoes.
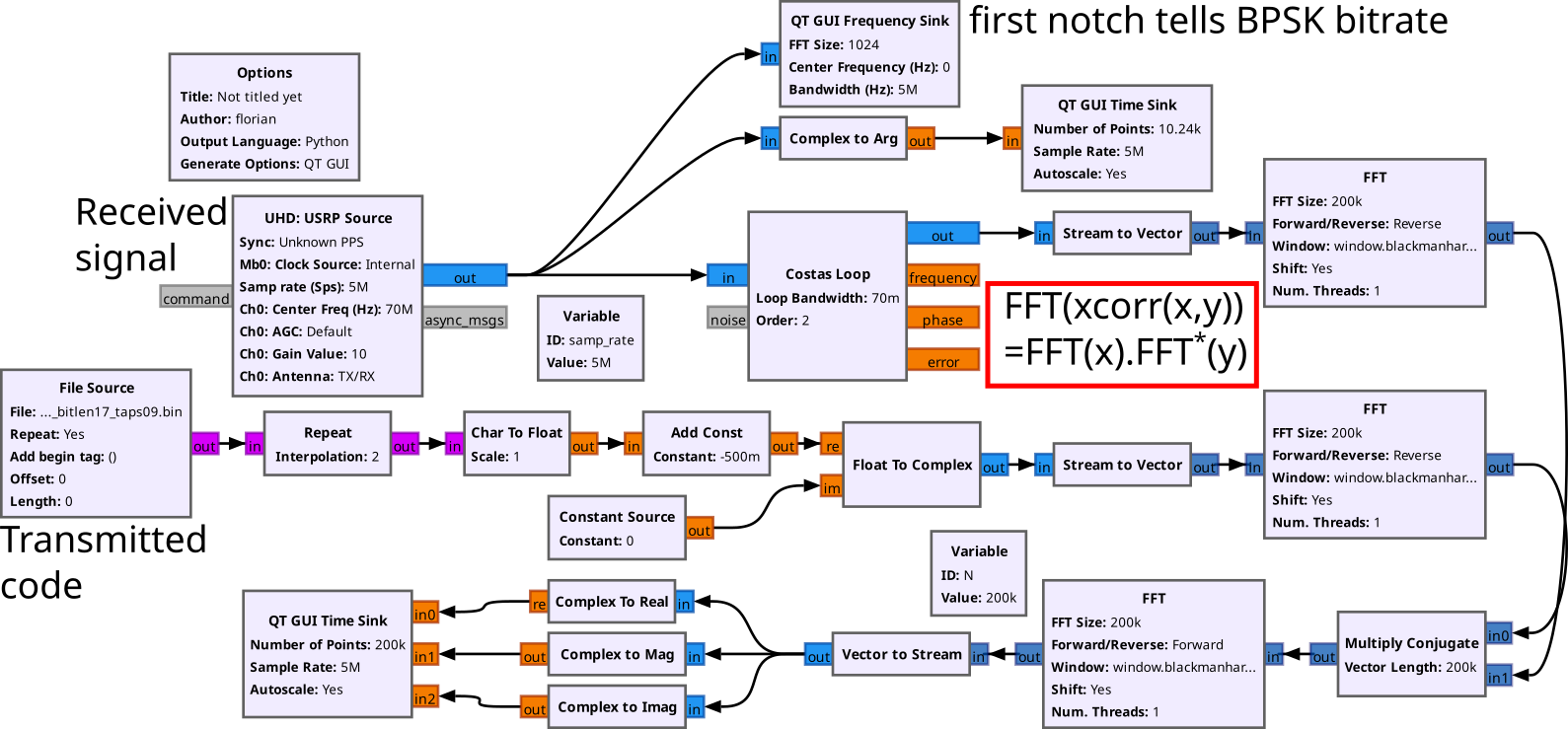
Saving lives is one of the most rewarding things you can do using SDR. In this presentation, we demonstrate a standards-compliant transceiver for the upcoming second generation of the COSPAS-SARSAT, and explain in depth how different approaches to frequency and phase synchronization can fundamentally improve receiver operational characteristics.
Two Ettus Research USRP hardware platforms are investigated for adding custom functionalities to the FPGA gateware: the B210 on the one hand, and on the other hand the X310 through the RFNoC framework. This presentation will demonstrate how to integrate a standalone, stream independant Verilog code either hand written or produced using Amaranth or LiteX, accessing Front Panel GPIOs for generating synchronization signals (1-PPS). A second demonstration will timestamp the datastream on an external synchronization signal.
SATRE is a proprietary modem commercialized by TimeTech and used for broadcasting pseudo-random sequences from ground to a geostationnary satellite for comparing clocks between time & frequency metrology laboratories. Similar to GPS, a digital communication code has been added on top of the CDMA code modulated as BPSK signals to transfer information including time and range from ground of each emitting station to the satellite. This signal is broadcast by European & American metrology institutes every even hours and decoding its content would open wide access to one-way time transfer, only requiring a television reception parabola and SDR receiver. Progress in decoding the code will be presented.
The current means of Two Way Satellite Time and Frequency Transfer relies on a closed, proprietary hardware developed in the 1980s and commercialized since by TimeTech GmbH with the SATRE modem. Beyond the little information available on the selected technology, few experiments have attempted to assess the limitation of current technological limitations, including coding length, coding scheme (BPSK) or pseudo-random sequence. We have developed an opensource portable framework for prototyping various means of selecting coding and modulation schemes aimed at assessing optimal conditions for sharing time and frequency in two-way communication, possibly adaptable to one-way communiction through the proposed open protocol. Preliminary results will be shared in addition to the technical details on signal acquisition and processing. Github: https://github.com/oscimp/amaranth_twstft
We present an implementation of a distributed multi-computer/multi-radio setup for synchronising USRP timing inside of the FIT/CorteXlab testbed, using Octoclocks.
In this presentation we will talk about some interesting experiences acquired while creating a dataset for radio fingerprinting concerning synchronization of radios in the CorteXlab experiemental testbed. These observations might help others designing datatsets in taking synchronization into consideration.
In this presentation we will talk about the use of GNU Radio to teach advanced concepts such as synchronization of locals oscillators, symbol synchronization and header correlation with student who do not have a significant background in mathematics.
The conference is now over: thank you for attending, a few pictures of the gathering.
|
 Don't panic: the conference goodie
Don't panic: the conference goodie Thomas Lavarenne teaching
Thomas Lavarenne teaching  Felix Artmann and Marcus Müller presenting SARSAT communication
Felix Artmann and Marcus Müller presenting SARSAT communication Paul Boven introducing the impact of local oscillator phase noise on coherent energy accumulation when computing correlations in the context of radioastronomy.
Paul Boven introducing the impact of local oscillator phase noise on coherent energy accumulation when computing correlations in the context of radioastronomy.
